
Layout, design and features …
Let’s first take a closer look at the Intel Core i9-14900K processor.
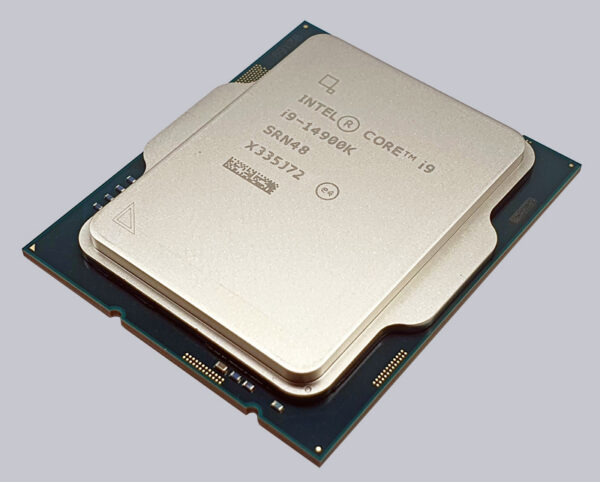

In addition to the type description, Intel laser-engraves the serial number, clock frequency and product code on the heatspreader.

The back of the CPU presents a familiar picture, because like all current Intel processors, the CPU is manufactured as an LGA version.

Intel Raptor Lake-S innovations …
The underlying product generation behind the Core i9-14900K is Raptor Lake-S in the Intel 7 manufacturing process. The 10nm Enhanced Super Fin is the latest process and Raptor Lake-S is now the 14th generation Raptor Lake-S after the 13th generation with the code name Raptor Lake from Intel. In addition to various fine-tuning and Intel Thermal Velocity Boost for the Core i9-14900K, the number of cores has been increased to 24, whereby the socket remains LGA1700 and the CPU therefore remains downwards compatible. If you still have an LGA1200 cooler, you will need new cooler brackets with modified holes for the LGA1700. Otherwise, PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 support remain with the Raptor Lake refresh, whereby a RAM clock rate of up to DDR5-5600 is now supported and even the previous DDR4 memory is retained on corresponding motherboards up to DDR4-3200.
Hybrid CPU with P-Core and E-Core …
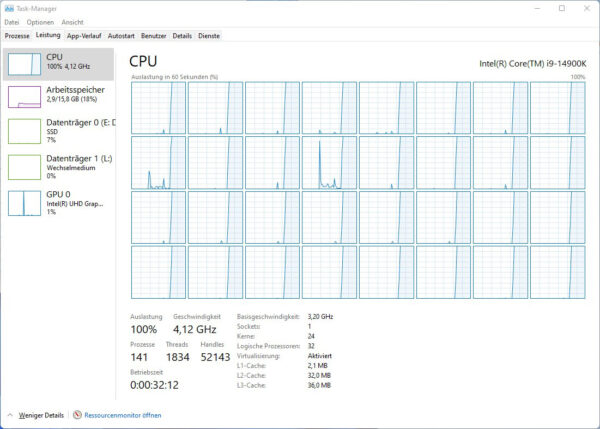
With some 14th generation Intel processors, there is again a distinction between a P-core and an E-core. These are the so-called Performance Cores and Efficient Cores, whereby the E-Cores work in the background at a lower frequency, while the P-Cores can perform the more demanding work in Windows or Linux. The following table shows which CPUs have E-cores. If you switch the performance display of the Task Manager to logical processors in Windows, you can clearly see the 24 cores of the Intel Core i9-14900K CPU, which are divided into 8 performance cores and 16 efficiency cores that work completely independently of each other. The 8 P cores are divided into 16 threads, giving us a total of 32 logical processors.
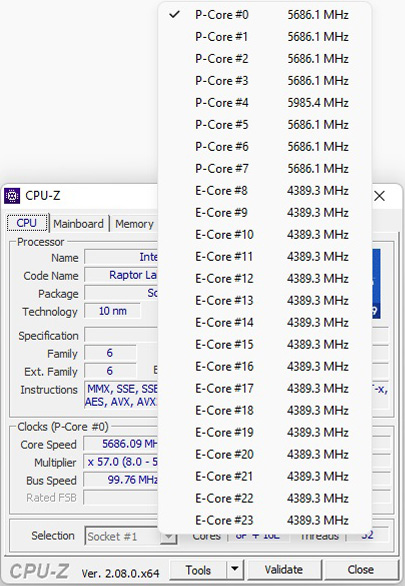
With the popular CPU-Z tool, you can display an overview of all P-core and E-core clock rates and immediately recognize the different clock rates of the P-cores and E-cores.
The following processors are currently available in the 14th generation:
| Overview of the Intel Raptor Lake-S processors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Cores | Threads | Clock | TDP | Max. Power | GPU |
| Intel Core i5-14600K | 6P/8E | 20 | 3.50-5.30GHz | 125W | 181W | UHD Graphics 770 |
| Intel Core i5-14600KF | 6P/8E | 20 | 3.50-5.30GHz | 125W | 181W | – |
| Intel Core i7-14700K | 8P/12E | 28 | 3.40-5.60GHz | 125W | 253W | UHD Graphics 770 |
| Intel Core i7-14700KF | 8P/12E | 28 | 3.40-5.60GHz | 125W | 253W | – |
| Intel Core i9-14900K | 8P/16E | 32 | 3.20-6.00GHz | 125W | 253W | UHD Graphics 770 |
| Intel Core i9-14900KF | 8P/16E | 32 | 3.20-6.00GHz | 125W | 253W | – |
In addition to the Intel Core i9-14900K with unlocked multiplier and 125-253W TDP that we tested, there are a few variants, such as the Intel Core i7-14700K with unlocked multiplier and 125W-253W TDP and the Intel Core i5-14600KF without integrated graphics unit. Processors with a locked multi or lower TDP, on the other hand, can still be found in the 12th and 13th generation.
Speaking of TDP, the power consumption including all components such as memory and SSD with integrated Intel UHD Graphics 770 GPU was 406.4 watts under full load and only 28.8 watts at idle, including ARGB motherboard bling-bling 
In terms of compatibility, the Intel Core i9-14900K works with the Intel H770, B760 and the Z790 chipset as well as the previous Intel W680, Q670, H610, H670, B660 and Z690 chipsets. With 28 lanes, the Z790 supports the most PCI-E lanes and up to 8 SATA 3.0 ports, whereas the B760 only supports 14 PCI-E lanes and 4 SATA 3.0 ports. It is interesting to note that Intel not only officially supports CPU overclocking for the Intel Z790 chipset, but also for the Intel H770 and B760 chipsets.
This brings us to the Intel Core i9-14900K installation …

