The term 3D printing is becoming more and more common and there are plenty of reasons for it. Because 3D printing can be used to produce a wide variety of things for all walks of life. Whether it’s a camera mount for the motorcycle or drone, a kitchen cutlery holder for the kitchen, or a sphere in which a hamster can explore the home. The possibilities are almost limitless. One thing is clear in any case. 3D printing has never been easier or more affordable. You do not need to be a computer specialist or mechanical engineer to operate a 3D printer at home. What you need to create even the most exciting creations is revealed here at OCinside.de in this workshop.
Thanks for the support …
Thanks for the support to Daniel.
Here you can buy 3D-printers at a reasonable price. *Ad
Introduction – What does 3D printing actually mean?
3D printing is technically an additive manufacturing process. This means that an ultimately solid, three-dimensional object is created layer by layer. Because the process and components are similar to a printer, it’s also called 3D printing.
The starting materials for this can be powder, liquids or solid materials such as plastic wires. The 3D printer takes this starting material into its final form during the manufacturing process. Because this is a workshop for newcomers to 3D printing, the following is a description of the more entry-level FDM process (also FLM or FFF).
The SLA process, where a laser forms liquid resin into a solid plastic model, is also applicable for home use. However, this printing technique requires some care in handling the materials and the available devices are rather designed for smaller objects. Therefore we will limit ourselves to the FDM process in this workshop, as we believe it is the best compromise for most applications.
What is the FDM process exactly?
The starting material for FDM 3D printing is a plastic wire called filament on a spool.
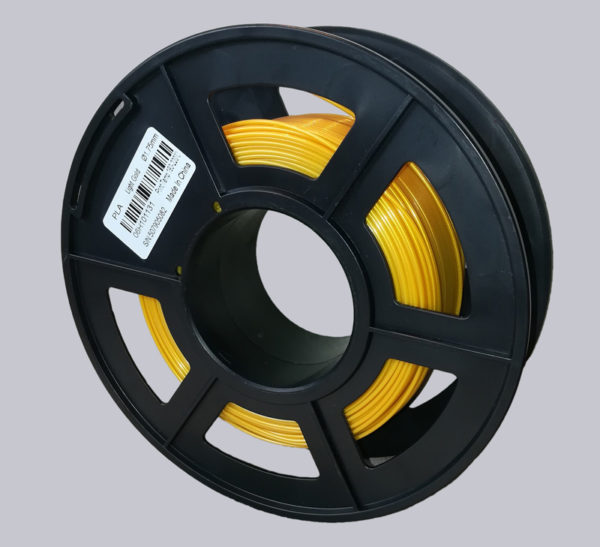

The filament is heated by the printer until it almost melts and then sprayed through a nozzle onto a carrier plate in layers. This is called extrusion. After emerging from the nozzle, the plastic solidifies rapidly, which means that it retains its shape and does not run away. This process can be used to produce extremely complex shapes that cannot be produced by conventional casting or machining methods. Even intertwined shapes and complex cavities can be produced with the FDM method.
To give you an idea of how a 3D printer prints, we have created a small video on our OCinside YouTube channel, or more precisely, cut it together so that it does not take so long.
Note: Please allow our cookies first to see this external content!
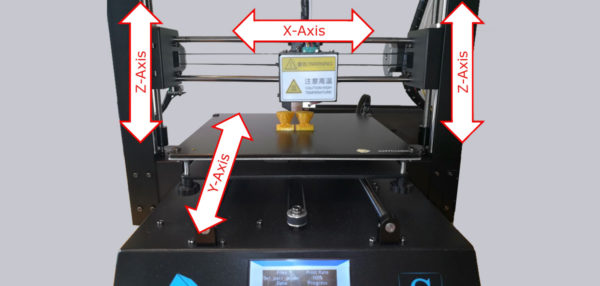
Next, let’s take a look at how a 3D printer is built …

